Radiation-induced Optic Neuropathy
- Sudden, irreversible visual loss from radiation-induced infarction of the intracranial optic nerve
- Occurs months to years after radiation therapy of paranasal sinus or cranial base tumors
- More likely if the total radiation dose exceeds 6000 cGy, the daily dose fraction exceeds 200 cGy, or there was faulty delivery technique
- Patients with arteriolar sclerosis, diabetes, neurofibromatosis Type 1 are at higher risk
- Afferent pupil defect is often the only objective clinical sign
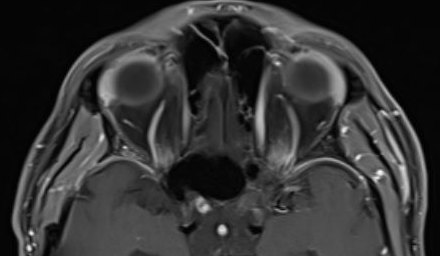
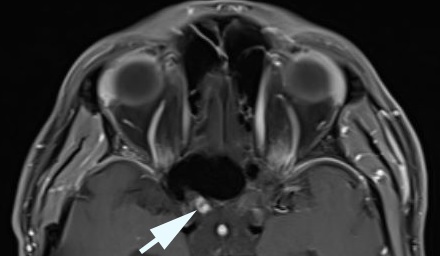
- MRI brain abnormalities are often distinctive
- No effective treatment, although corticosteroids and hyperbaric oxygen are often proposed
- Acute painless visual loss, usually monocular, but step-wise visual decline is common
- Subnormal visual acuity
- Nerve fiber bundle or hemianopic visual field defects
- Eyes and surrounding tissues appear structurally normal
- Afferent pupil defect
- Brain MRI shows sharp-margined enhancement and thickening of the intracranial optic nerve near the optic chiasm
- Optic neuritis
- Infiltrative optic neuropathy
- Compressive optic neuropathy
- Hypotensive optic neuropathy
- Order brain MRI to exclude compressive, inflammatory, and infiltrative causes and to confirm the classic imaging sign of radiation optic neuropathy
- Consider lumbar puncture if the diagnosis remains uncertain
-
Trap: high-dose corticosteroid, anticoagulation, and hyperbaric oxygen treatments are often prescribed but support for their benefit is very weak

- No effective treatment
- Vision loss is irreversible, and further visual loss may occur from repeated infarction over weeks to months