Posterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Acute monocular or binocular retrobulbar optic nerve infarction with a normal-appearing optic disc
-
Causes
- Systemic hypotension (See Hypotensive Ischemic Optic Neuropathy )
- Cranial irradiation (See Radiation-induced Optic Neuropathy )
- Intracranial surgery or endovascular procedure
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Sino-orbital fungal infection
- Granulomatous polyangiitis
- Giant cell arteritis (See Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy )
- Lupus erythematosus
- Relapsing polychondritis
- Polyarteritis nodosa
-
Core features
- Painless acute monocular (less commonly binocular) loss of vision
- Visual acuity is normal or depressed
- Nerve fiber bundle visual field defects
- Afferent pupil defect unless vision loss is equal in both eyes
- Ophthalmoscopically normal-appearing optic disc
- Predisposing condition should be evident, most commonly systemic hypotension
-
Possible accompanying features
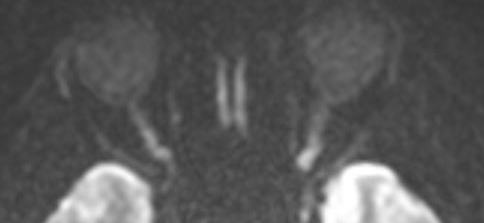
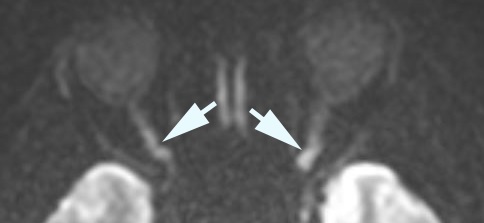
- MRI retrobulbar optic nerve enhancement, high T2/FLAIR and thickening, or restricted diffusion
- Radiation-induced optic neuropathy
- Hypotensive optic neuropathy
- Optic neuritis
- Arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy
- Compressive optic neuropathy
- Infiltrative optic neuropathy
- Paraneoplastic optic neuropathy
- Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
- Chiasmal and retrogeniculate visual loss (but should show hemianopic rather than nerve fiber bundle visual field defects)
- Exclude arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy in all elderly patients
- Look for provocative settings
-
Trap: do not make this diagnosis unless a provocative setting is evident
- Perform orbit/brain MRI primarily to exclude a non-ischemic cause
- Provide treatment based on the cause
- Visual prognosis depends on the cause and on how much damage has occurred