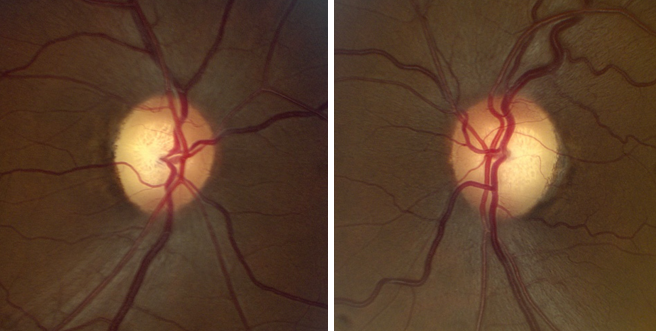
Dominantly-Inherited Optic Neuropathy
- Dominantly-inherited, binocularly symmetrical optic neuropathy caused by a chromosomal mutation at 3q (OPA1)
- Visual deficit may be mild or moderate and only minimally progressive
- No treatment
-
Core clinical features
- Patients are often unaware of reduced vision
- Diagnosis is often prompted by a failed vision screening examination or when family members are identified as having this condition
- Visual acuity gradually falls equally in both eyes but not below 20/200 (6/60, 0.1)
- Bilateral central or centrocecal scotomas
- Diffuse or wedge-shaped temporal optic disc pallor in both eyes
-
Possible accompanying clinical features
- Nystagmus
- Sensorineural hearing loss
-
Imaging features
- Brain imaging is normal or shows reduced optic nerve caliber bilaterally
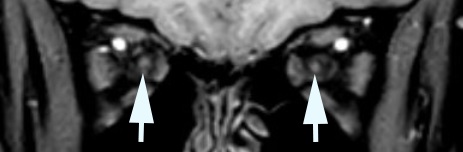
- Compressive optic neuropathy
- Toxic optic neuropathy
- Nutritional deprivation optic neuropathy
- B12 deficiency
- Hereditary photoreceptor degeneration
- Optic neuritis
- Psychogenic visual loss
- Order brain imaging to rule out a compressive optic neuropathy even if all findings are classic, including a clear family history
- Order genetic studies and counseling if appropriate
- Provide low vision aids
- Visual loss will often stabilize by the end of the first decade of life
-
Tip: other genetic causes and pedigrees of childhood optic neuropathy, other than OPA 1, are being reported