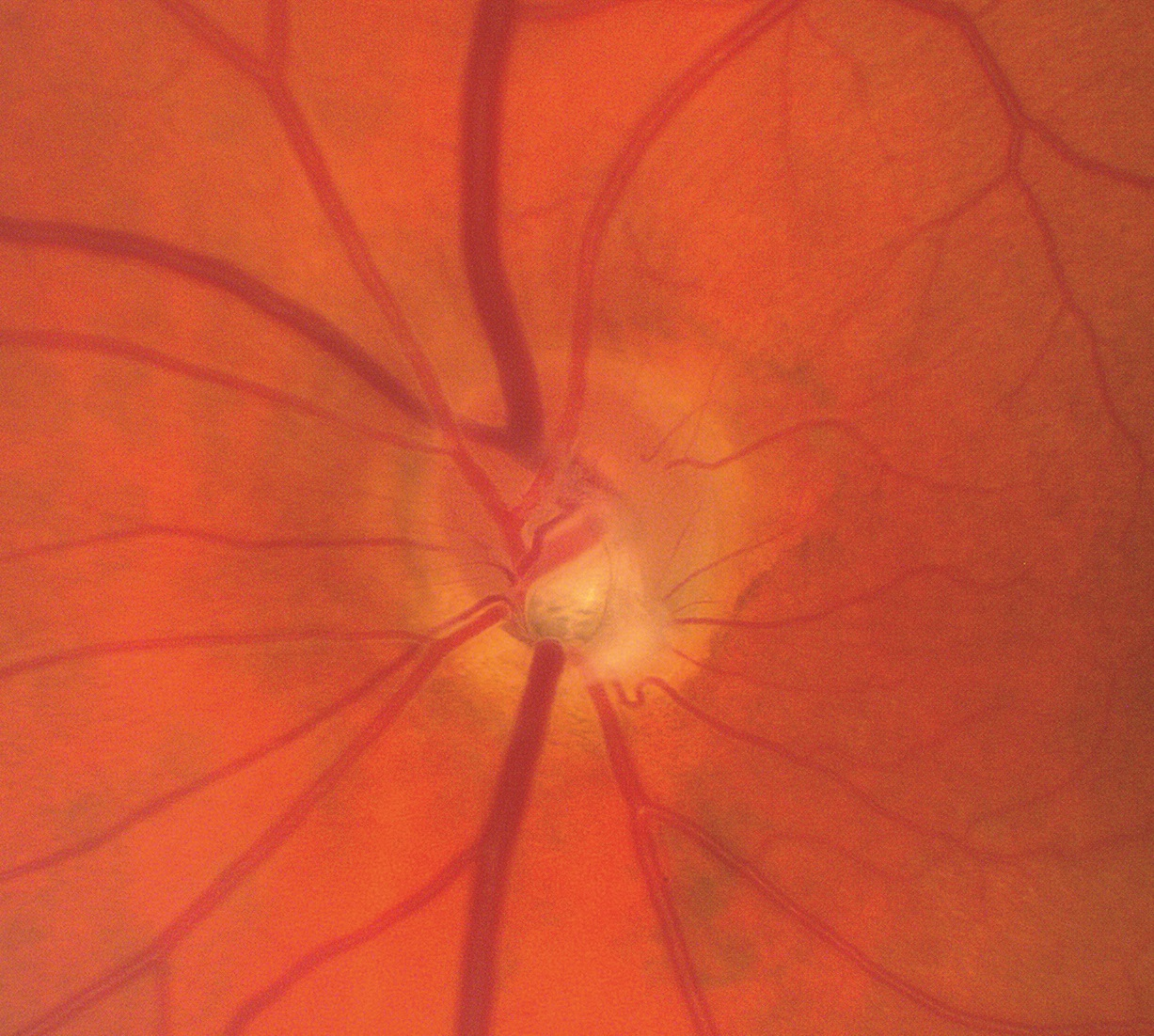
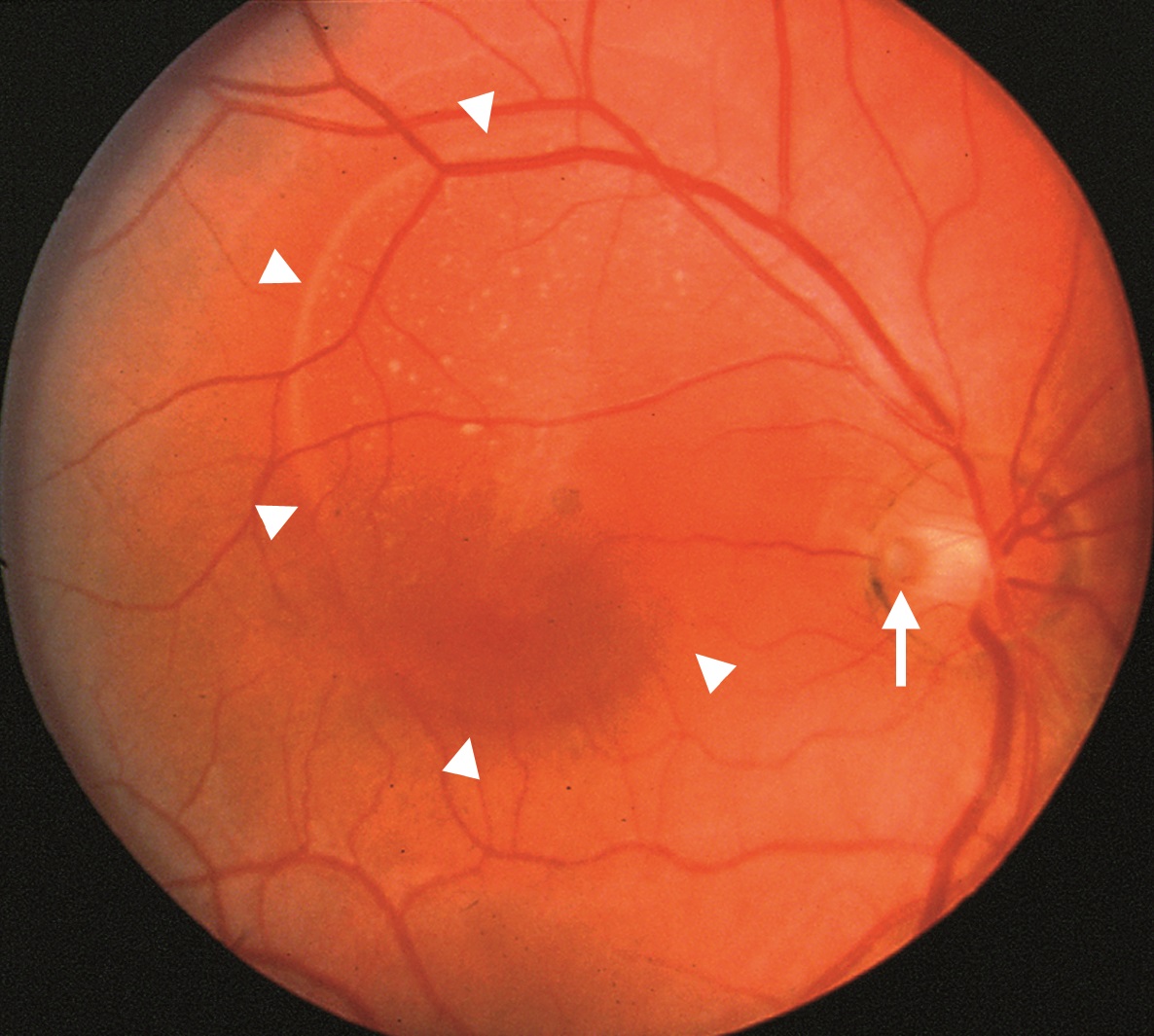
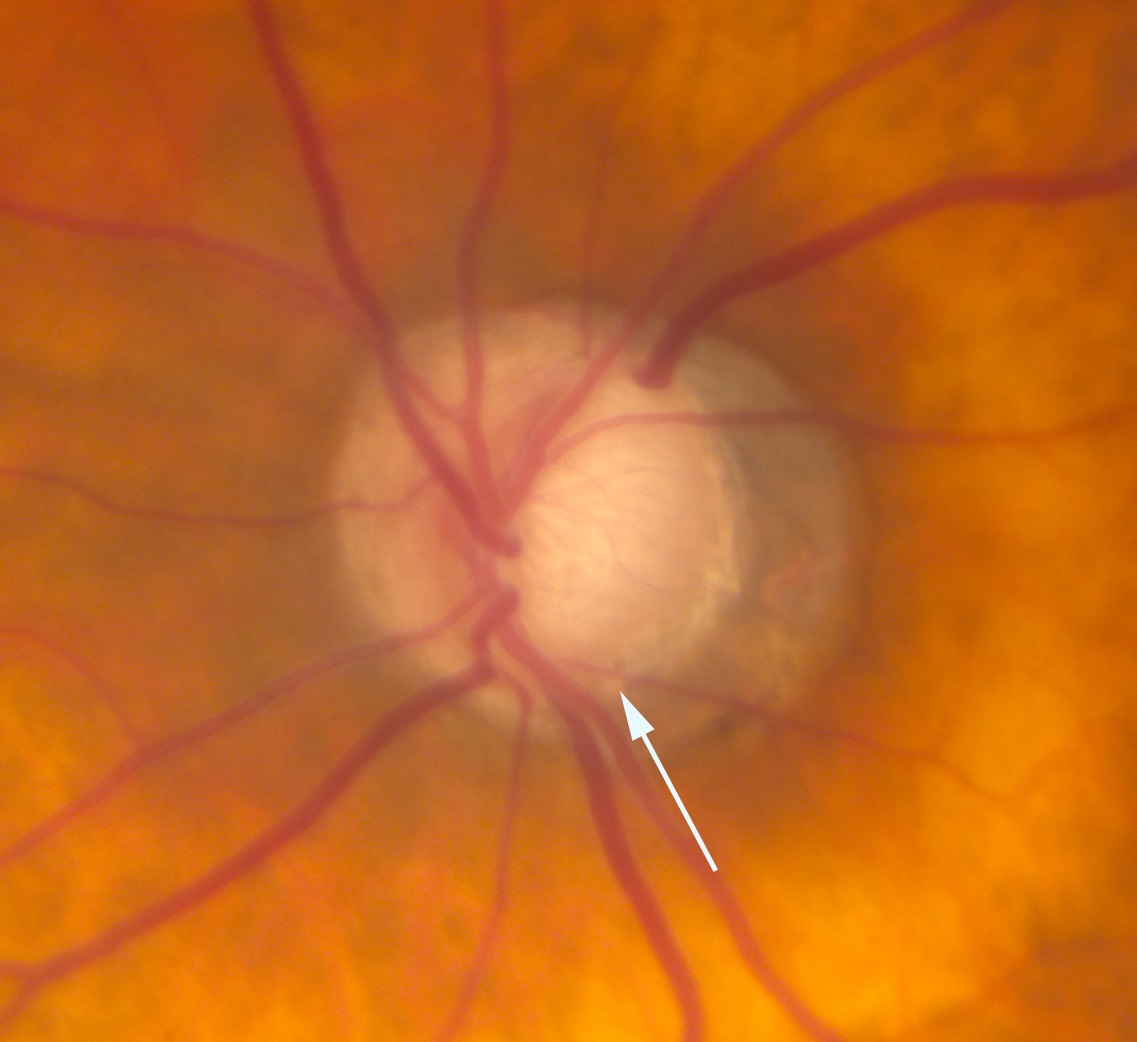
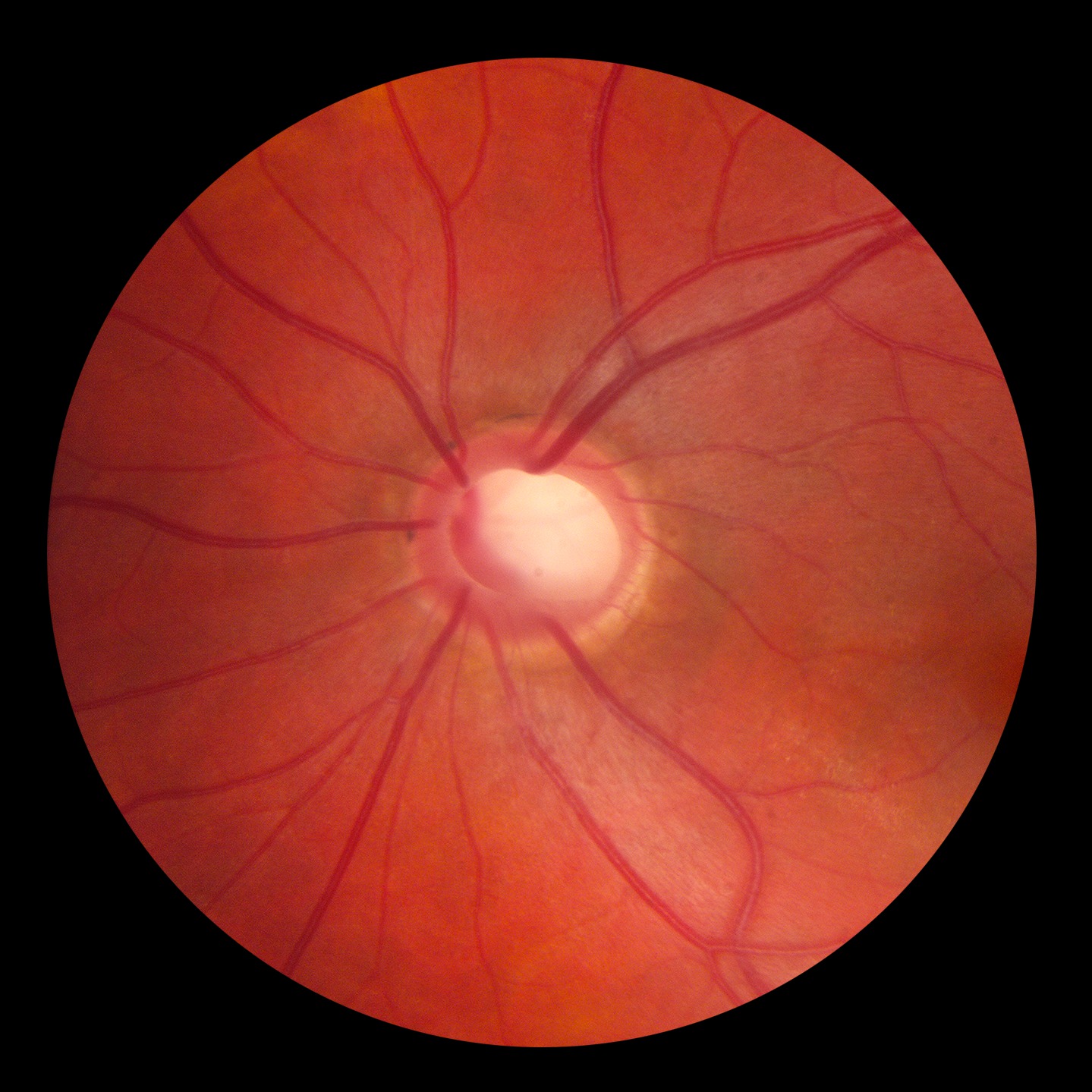
Optic Pit Neuropathy
- Congenital hole in the optic disc attributed to faulty embryogenesis
- Non-progressive visual field defect caused by absent optic nerve axons
- Look for an optic pit as the explanation for macular fluid or an unexplained visual field defect
- Optic pit and visual field defect remain stable
- Macular serous detachment may require photocoagulation or vitrectomy
-
Trap: optic pit is often misdiagnosed as glaucoma and unnecessarily treated