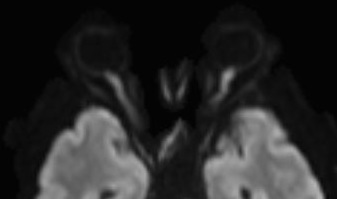
Hypotensive Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Infarction of the optic nerve caused by acute systemic hypotension
- Arises most commonly after prolonged prone-position lumbar spine surgery, cardiac and other non-ophthalmic procedures, acute septic and non-septic systemic hypotension
- Vision loss may spontaneously improve
- No effective treatment
-
Core features
- Painless vision loss in one eye or both within days of systemic hypotension
- Visual acuity and/or nerve fiber bundle visual field loss
- Afferent pupil defect unless both eyes are affected equally
- Optic discs appear normal ophthalmoscopically or show acquired elevation
- No other pertinent clinical findings
- Orbit and brain MRI may be normal or show restricted diffusion in the orbital segment of the affected optic nerves
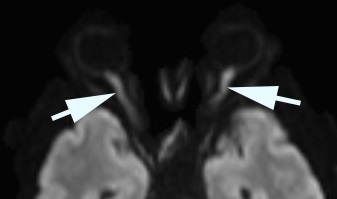
- Arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy
- Typical optic neuritis
- Atypical optic neuritis
- Compressive optic neuropathy
- Radiation-induced optic neuropathy
- Chiasmal and retrogeniculate vision loss (but should show hemianopic rather than nerve fiber bundle visual field defects)
- Perform MRI to exclude alternative retrobulbar causes
- Perform lumbar puncture only if there was no preceding episode of systemic hypotension
- Correct systemic hypotension to prevent further vision loss
-
Trap: do not prescribe hyperbaric oxygen treatment, which is often invoked in desperation but has been proven to be ineffective
- Vision may improve within weeks but substantial vision loss usually persists