Optic Radiation Lesions

-
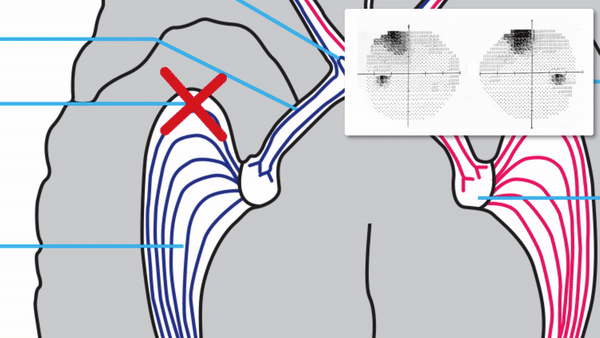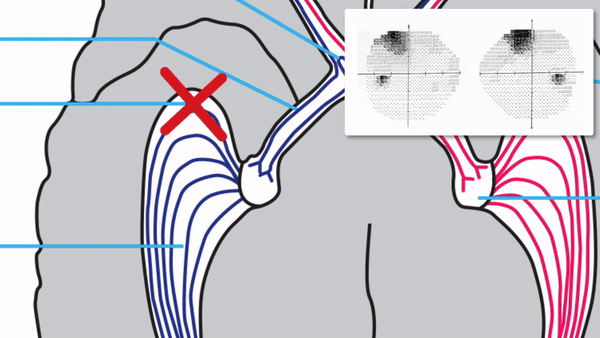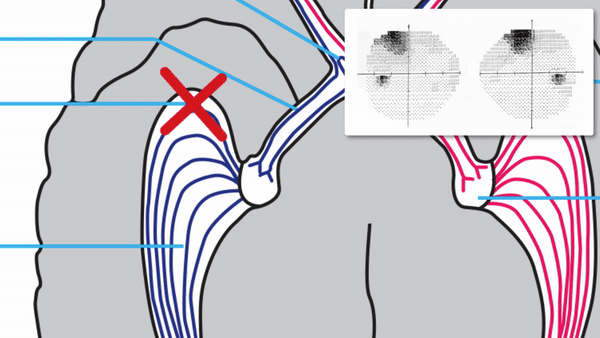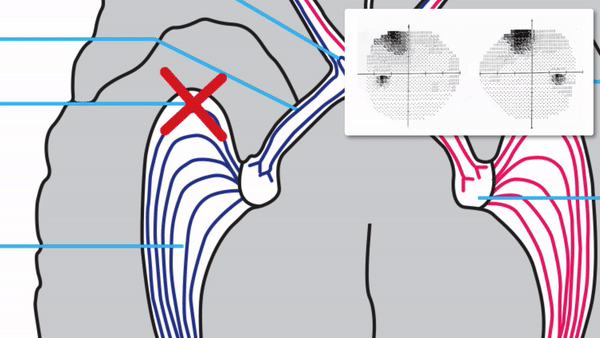
Focal damage to the optic radiations
-
Causes: neoplasm, head trauma, neurosurgical procedures, stroke, inflammation, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES)
-
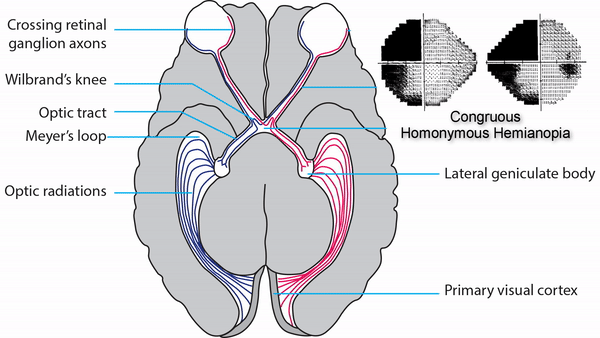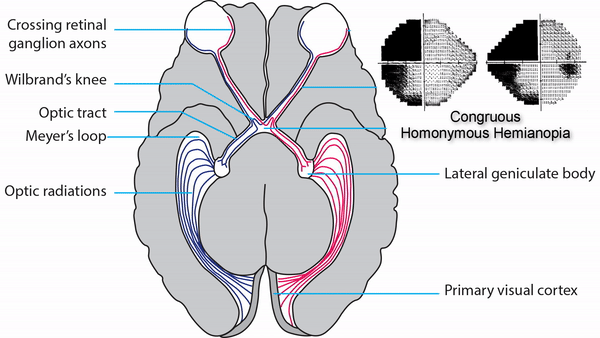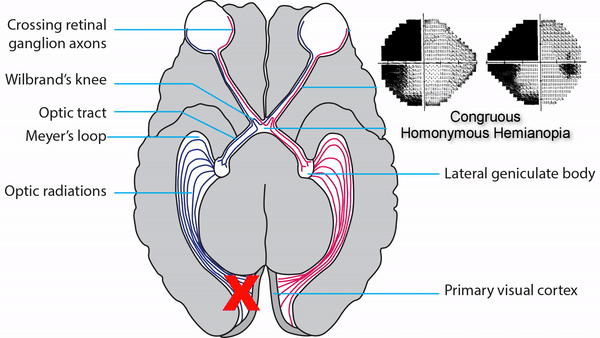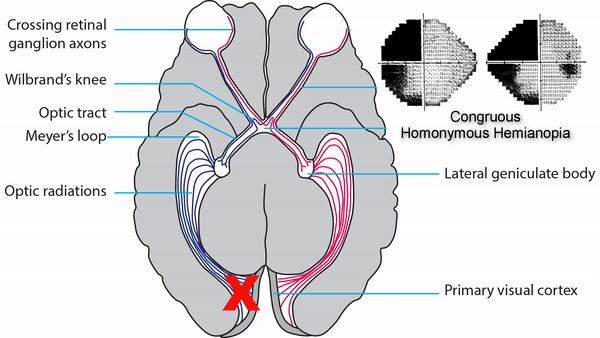
Complete or incomplete homonymous hemianopia that may be unilateral or bilateral
-
With unilateral incomplete homonymous hemianopias, look for the following localizing features
-
Congruous homonymous hemianopia
-
Superior wedge-shaped (“pie-in-the-sky”) defects indicate a lesion in the anterior temporal lobe (Meyer’s Loop)
-
Superior-dominant defects indicate a lesion in the temporal lobe
-
Inferior-dominant defects indicate a lesion in the parietal lobe
-
Brain MRI usually shows the lesion
-
Complete homonymous hemianopias localize to the retrochiasmal pathway but not to a particular location within that pathway
-
Perform visual fields on patients whose visual complaints are unexplained by ocular abnormalities
-
Look for localizing features on visual fields to differentiate between lesions of Meyer’s loop, posterior temporal lobe, and parietal lobe
-
Use visual field results and accompanying neurologic manifestations to direct imaging attention to the expected location of the lesion
-
Treatment depends on the cause