Dealing With The Constricted Visual Field
- Visual field that does not expand to its normal boundaries
-
Recognize the seven variants of this phenomenon
-
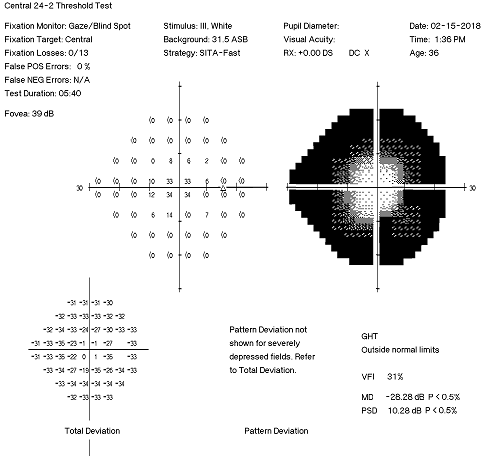
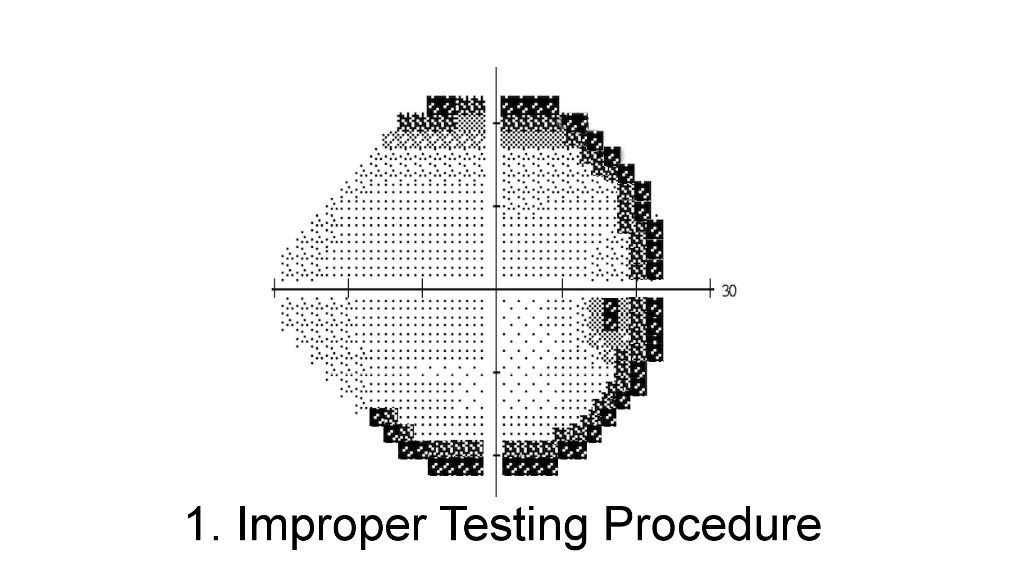
Improper testing procedure
- Defects consist of high thresholds around the edge of the visual field
- Usually due to an erroneous refractive correction, improper placement of the lens correction, or remote positioning of the patient’s head
- Redo the visual fields, correct any technical errors, clarify instructions to the patient, and encourage alertness to stimuli
- If the visual field remains constricted after these efforts, test by confrontation or kinetic perimetry
-
Reduced palpebral fissure height
- Defects consist of high thresholds around the edge of the visual field
- Due to ptosis, dermatochalasis, blepharospasm, or blepharophimosis
- Repeat the visual field test with the upper lid taped up
-
Patient inattention
- Generalized field constriction
- Usually generated by dementia, sleepiness, attention deficit disorder, other encephalopathy
- In dementia, inattention is probably based on poor disengagement of fixation
-
Extensive optic neuropathy
- Defects display steps across the nasal horizontal meridian (nasal steps)
- Most common in glaucoma, ischemic optic neuropathy, post papilledema optic neuropathy, and optic neuritis
-
Bilateral visual cortex lesions
- Defects are congruous with steps across the nasal vertical meridian with macular sparing ("keyhole fields")
- MRI usually reveals obvious lesions, typically effects of infarction
-
Retinal dystrophy
- Defects appear as incomplete rings usually centered between 20 and 40 degrees eccentric to fixation
- Full extent of the defects may not appear unless perimetry assesses the visual field beyond 30 degrees
- No step-offs along the horizontal or vertical meridians
- Ophthalmoscopy often shows retinal pigmentary abnormalities
- Electroretinography shows the characteristic abnormalities of outer retinal degeneration
-
Tip: paraneoplastic and other autoimmune outer retinopathies can display these ring defects and show little if any optic fundus abnormalities; disease progression is more rapid than in retinal dystrophies
-
Deliberate non-cooperation by the patient
- Any constriction pattern may appear
- Clover leaf pattern is common
- Progressive narrowing of the visual field occurs as kinetic perimetry proceeds ("spiraling")
- On confrontation testing, the visual fields do not expand as the testing distance increases (“tunnel field”)
-
Trap: before you blame deliberate non-cooperation, exclude procedural and organic causes!
-
Improper testing procedure