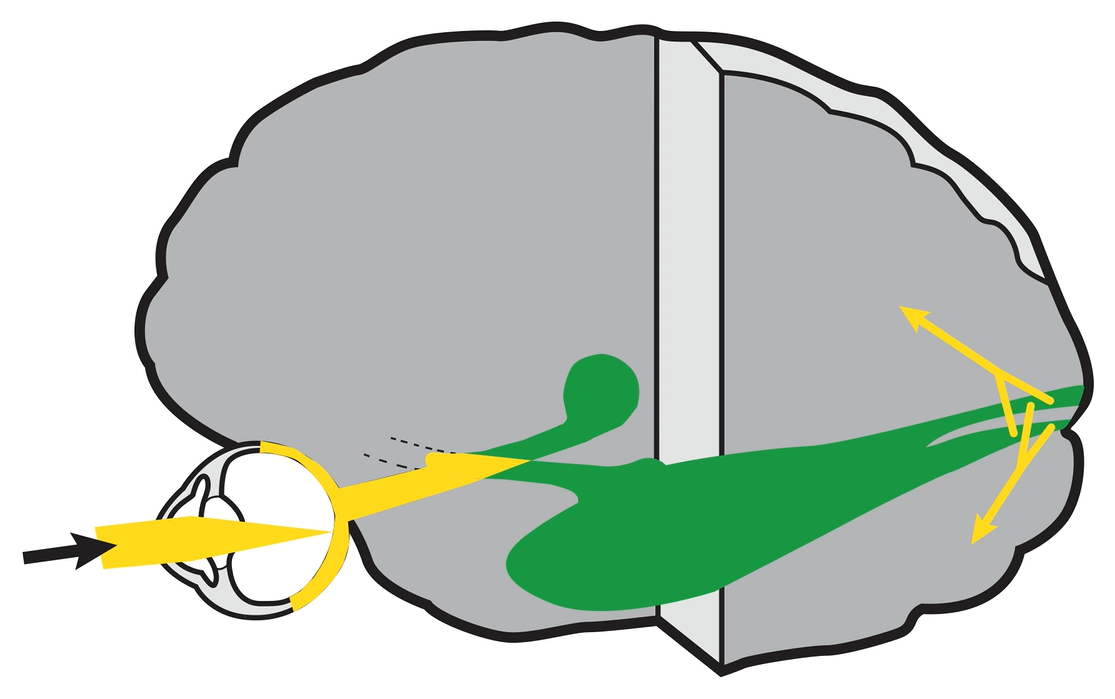
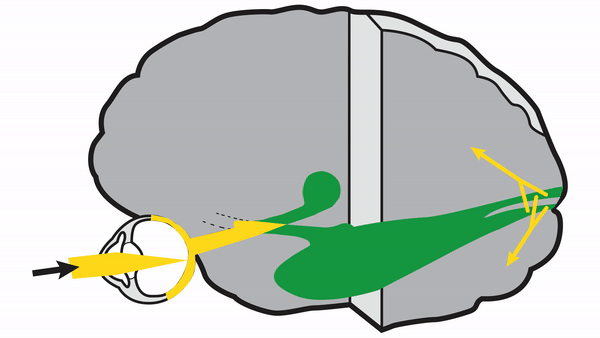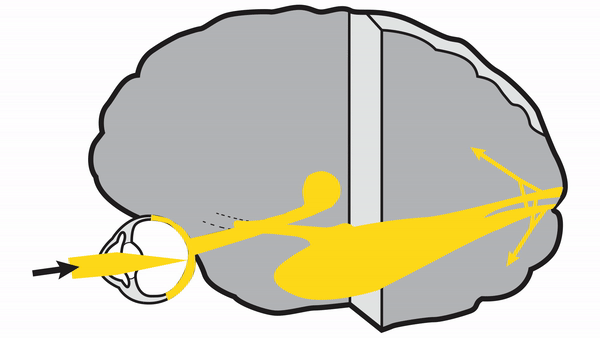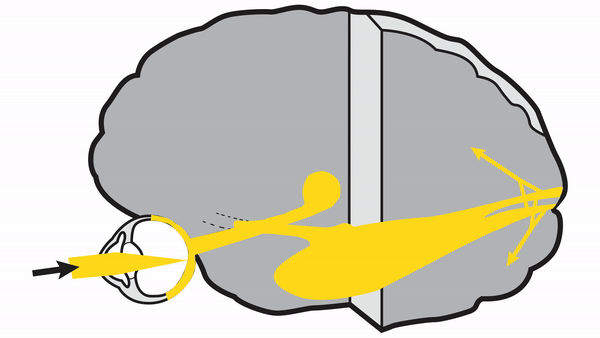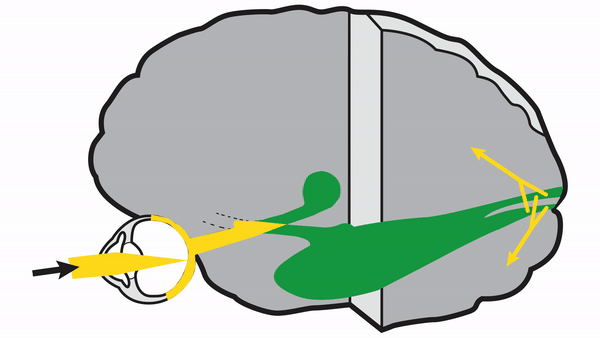
Retrochiasmal Segment
-
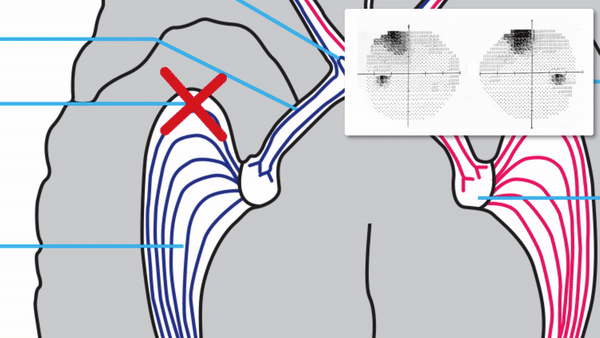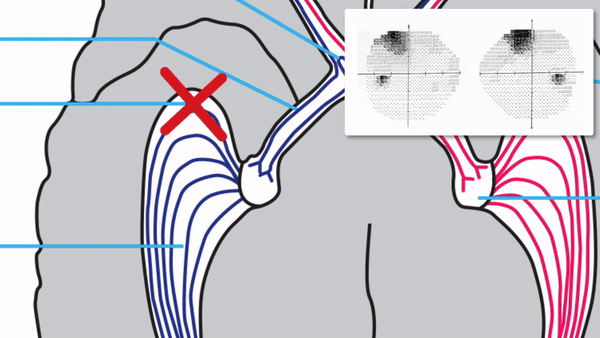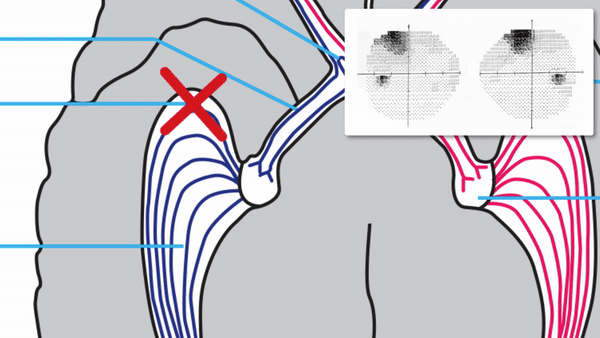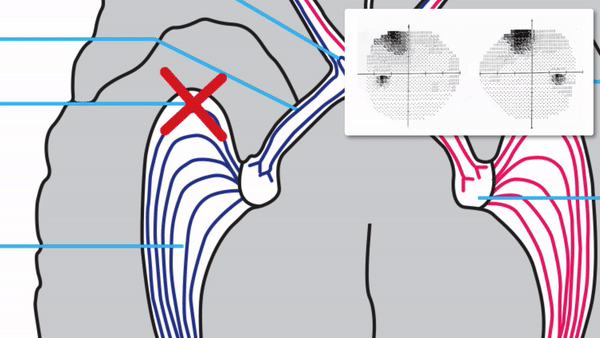
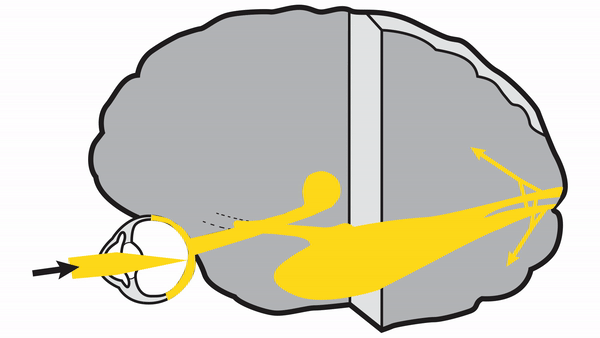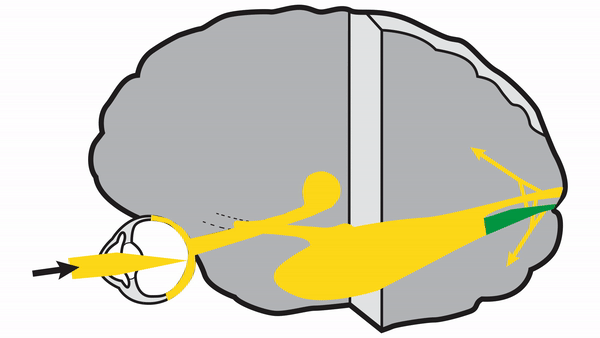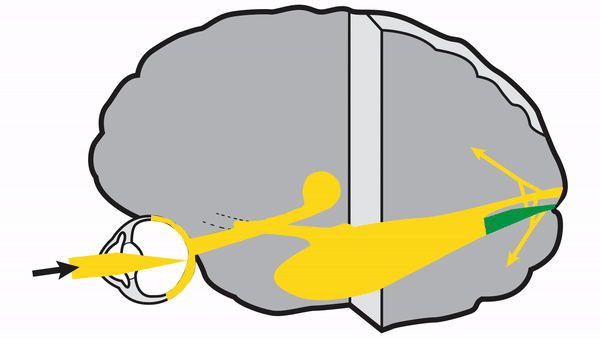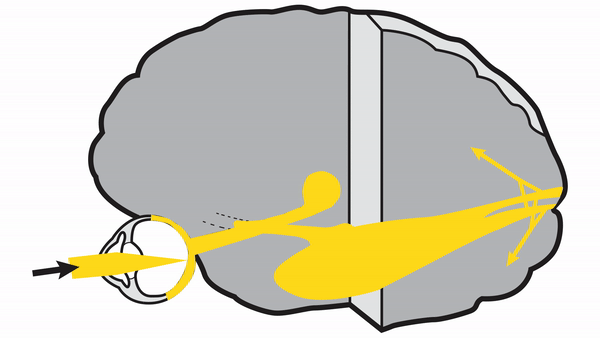
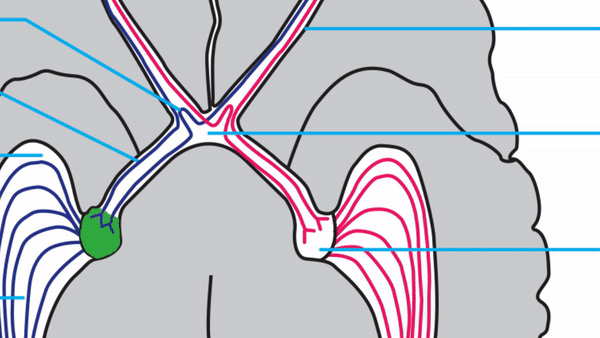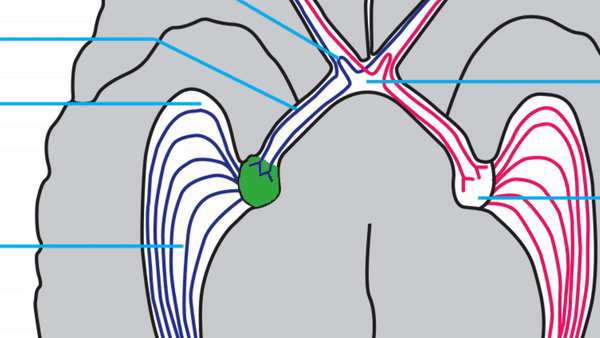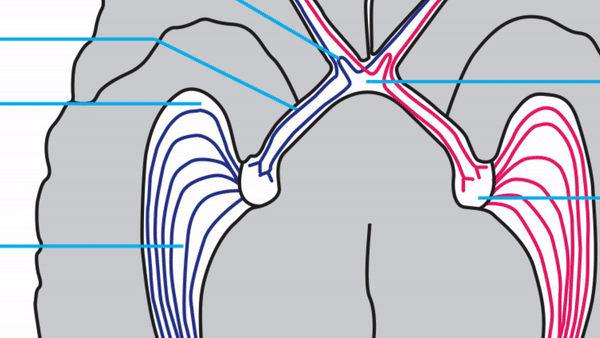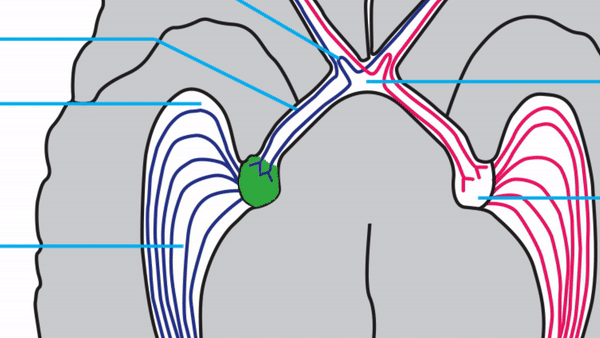
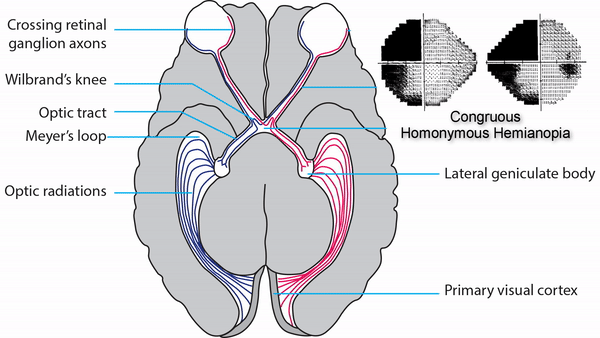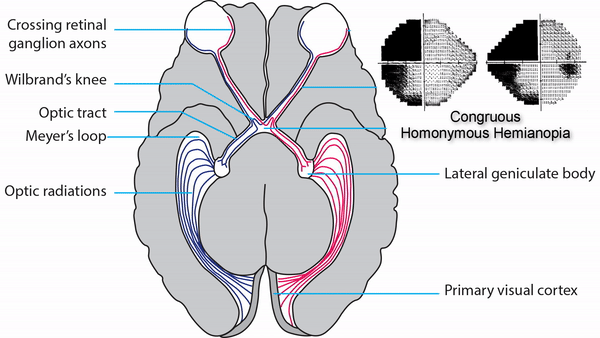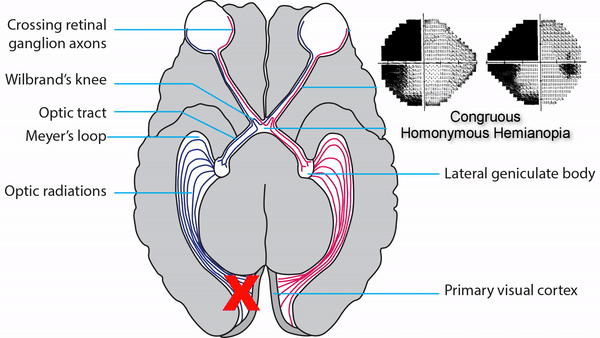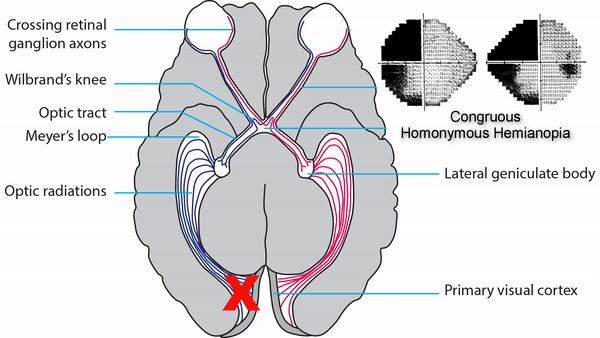
Optic tract
- Conveys signals from the opposite visual hemifield to the lateral geniculate body
-
Lateral geniculate body
- Contains synapses for signals coming from the optic tract
- Maintains segregation of signals from each eye, as signals from the ipsilateral eye terminate in layers 2,3, and 5, while signals from the contralateral eye terminate in layers 1,4, and 6
- Modifies signals by means of descending attentional and limbic input from the cerebrum
-
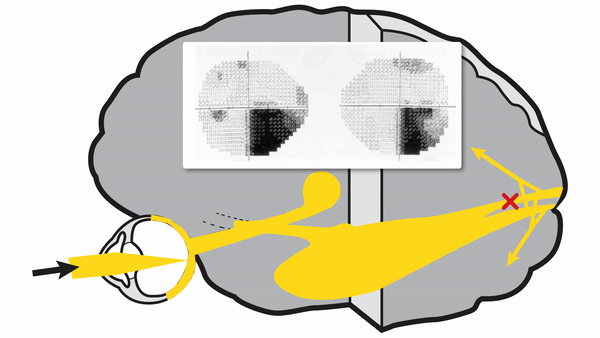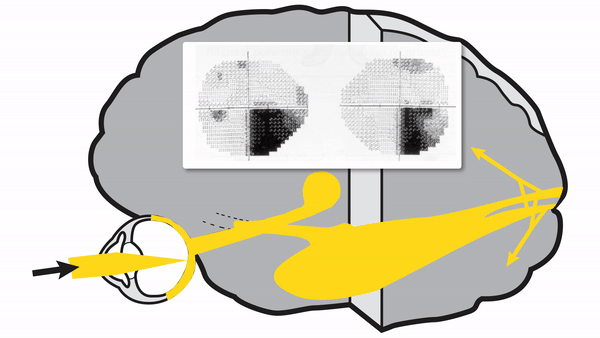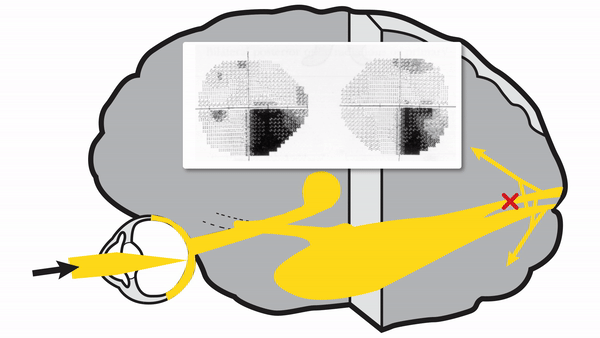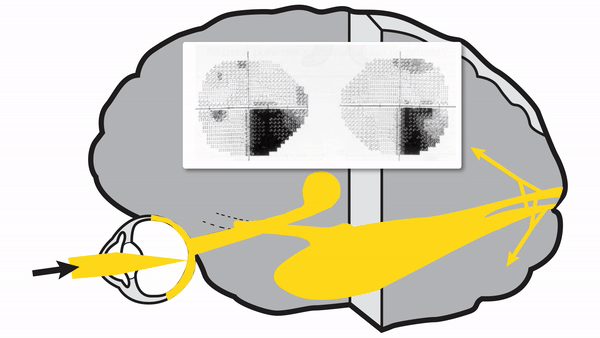
Optic radiations
- Contain axons exiting from the lateral geniculate bodies
- Some axons loop around the anterior temporal horn of the lateral ventricle as Meyer’s Loop
- Meyer’s Loop axons rejoin the rest of optic the radiations, which form a wide band along the border of the lateral ventricle, eventually dividing into superior and inferior forks at the atrium of the lateral ventricle
- Superior fork of the optic radiations enters the superior portion of the primary visual cortex
- Inferior fork of the optic radiations enters the inferior portion of the primary visual cortex
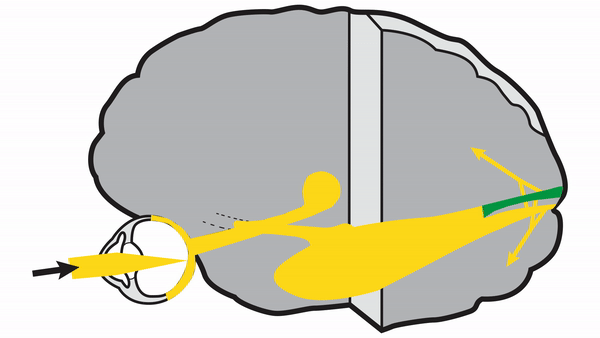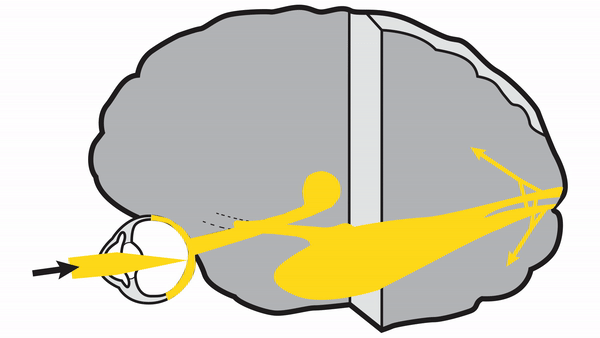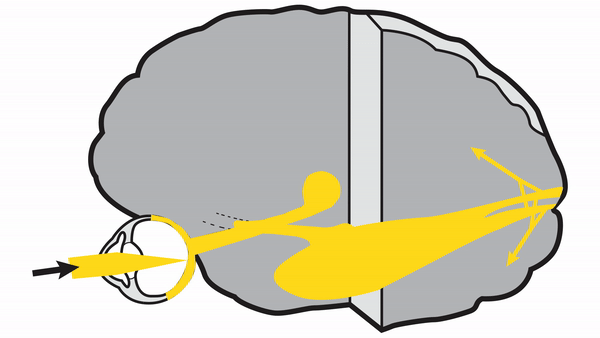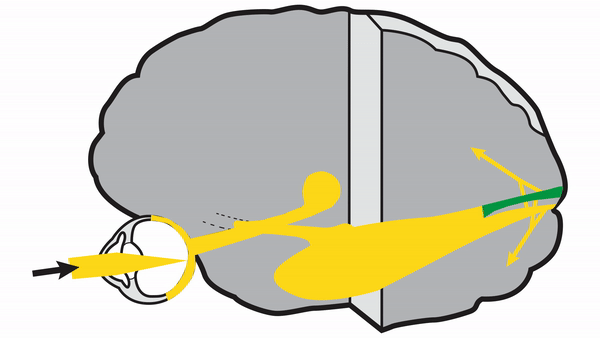
-
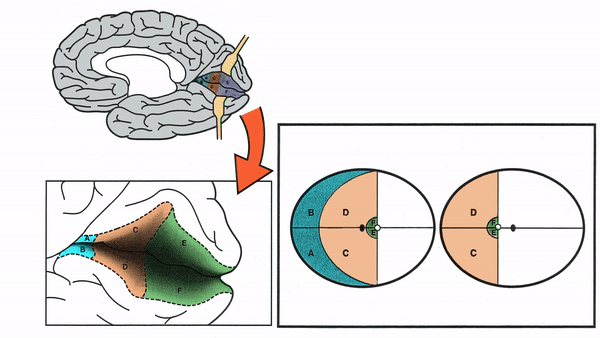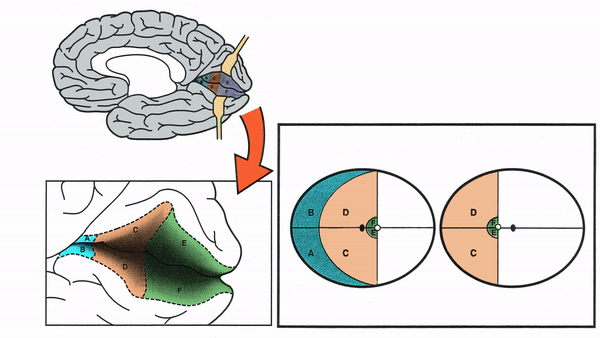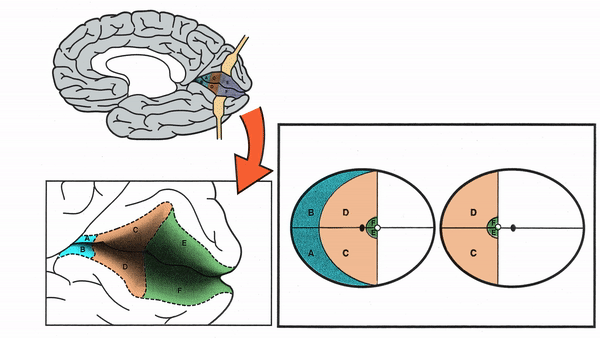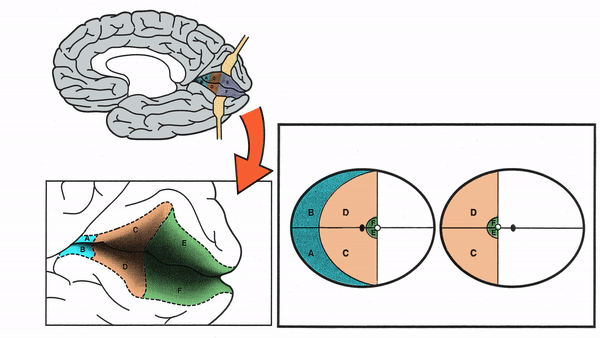
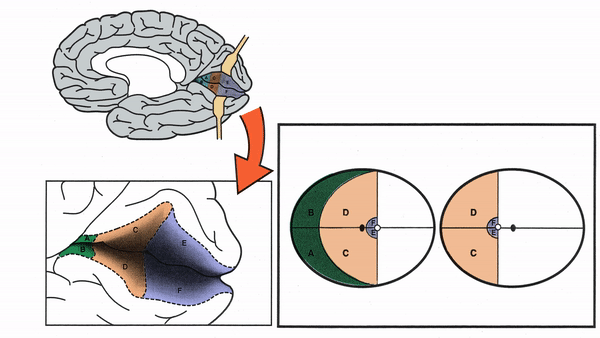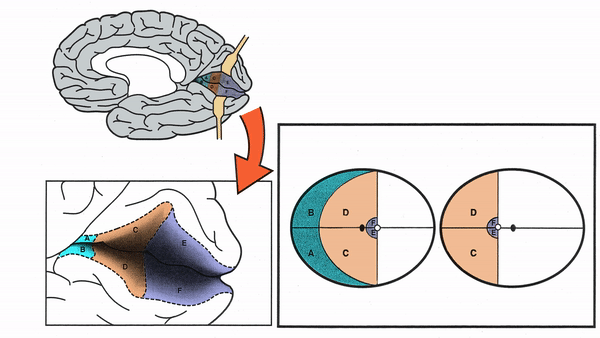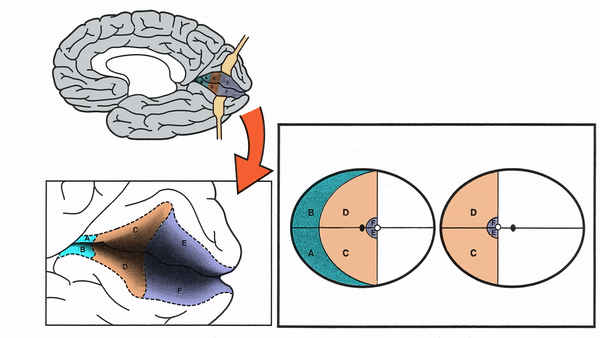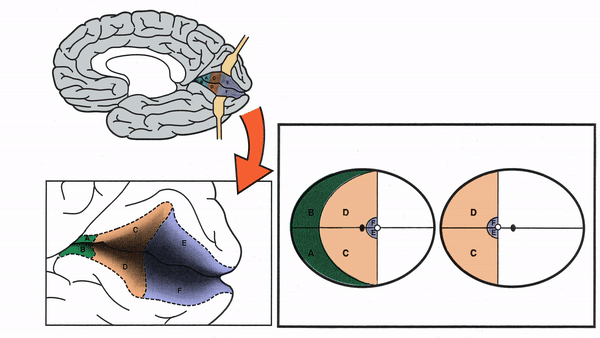
Primary Visual Cortex
- Signals coming from the central 5-10 degrees of the visual field terminate in the posterior visual cortex
- Signals coming from between 10 degrees and 60 degrees eccentric to fixation terminate in the intermediate primary visual cortex
- Signals coming from beyond 60 degrees (“unpaired temporal crescent”) terminate on the anterior visual cortex

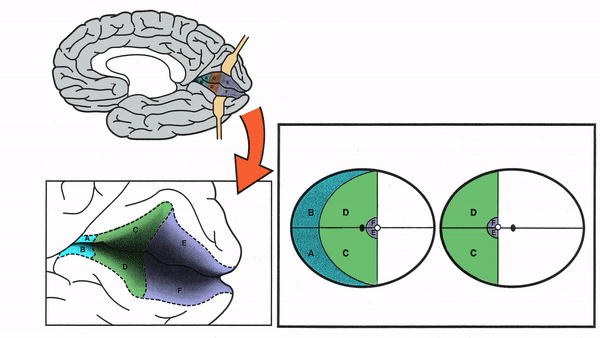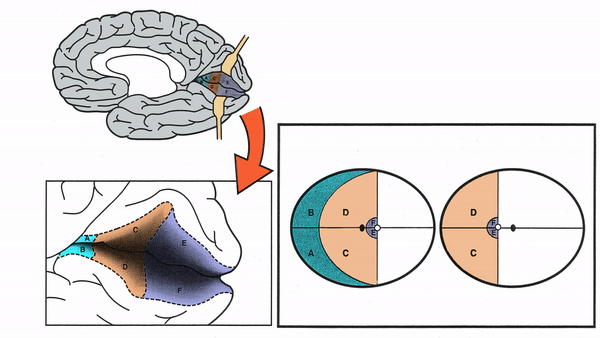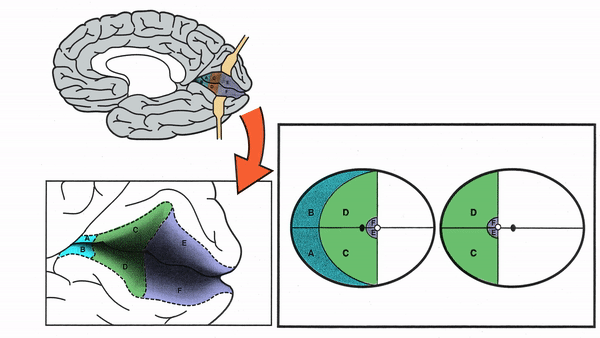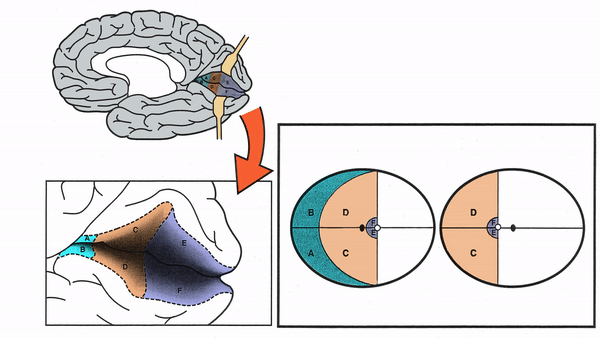
-
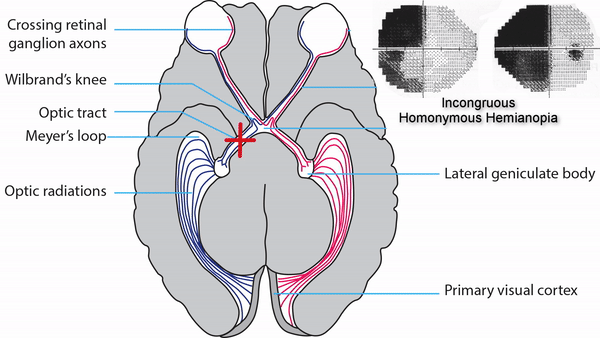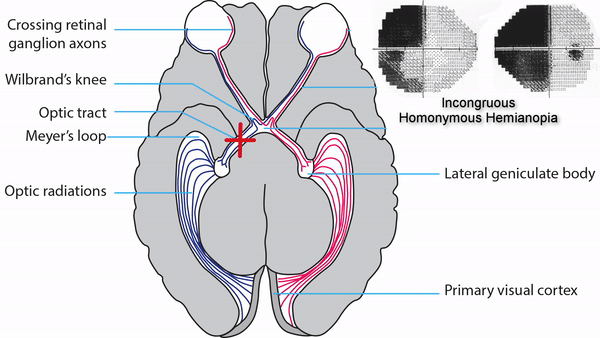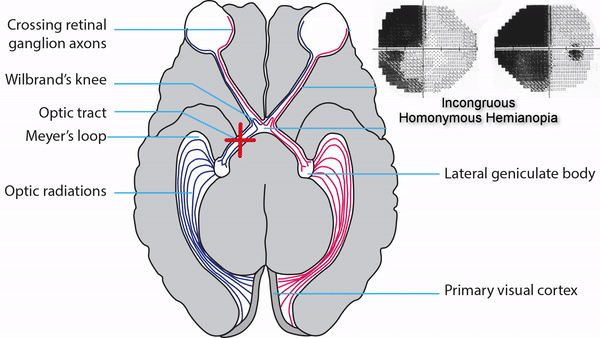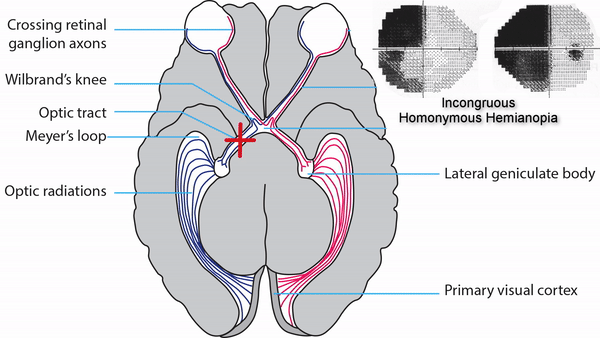
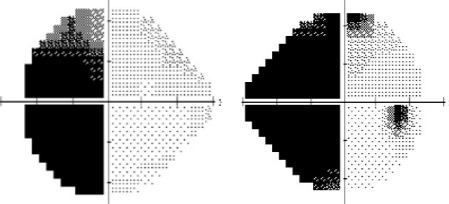
Optic tract lesions
- May produce either complete homonymous hemianopia (total damage) or incomplete but incongruous homonymous hemianopia (subtotal damage)
-
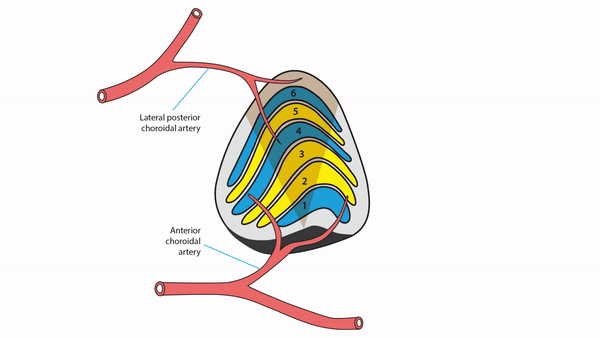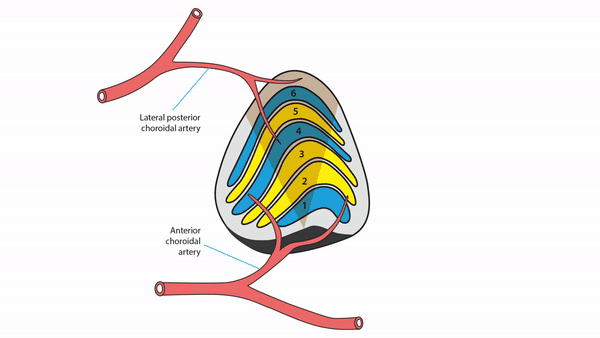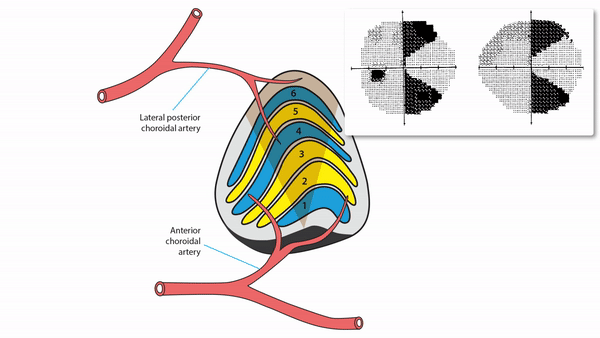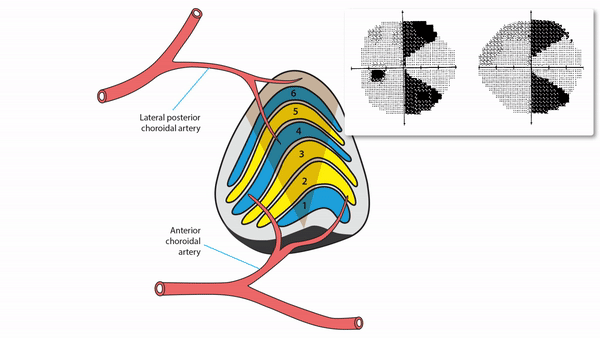
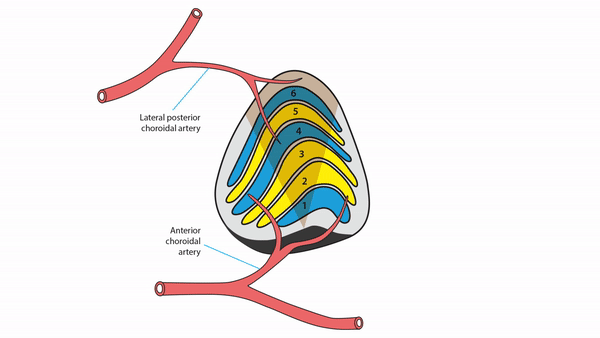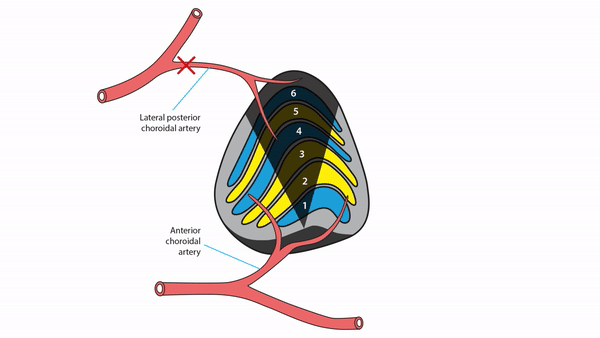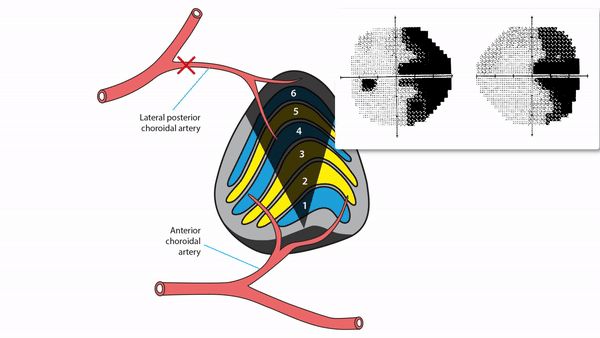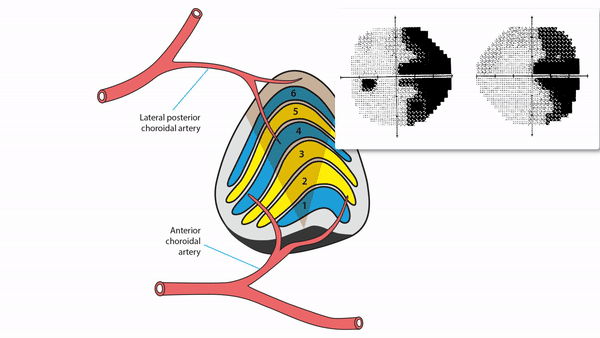
Lateral geniculate body lesions
- Mass lesions usually cause damage that extends beyond these small structures, destroying the entire lateral geniculate body, and causing complete homonymous hemianopias
- Anterior choroidal artery occlusion or lateral choroidal artery occlusion may produce hourglass homonymous hemianopias
-
Tip: inflammation and infarction may target BOTH lateral geniculate bodies in isolation

-
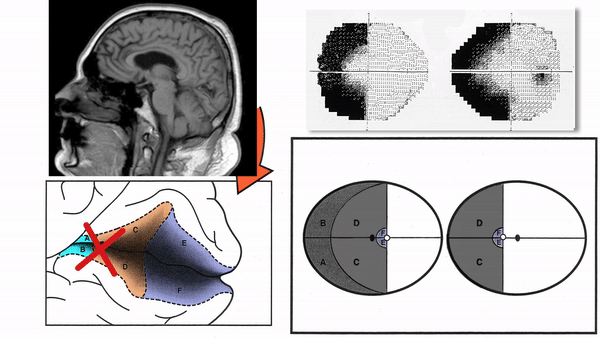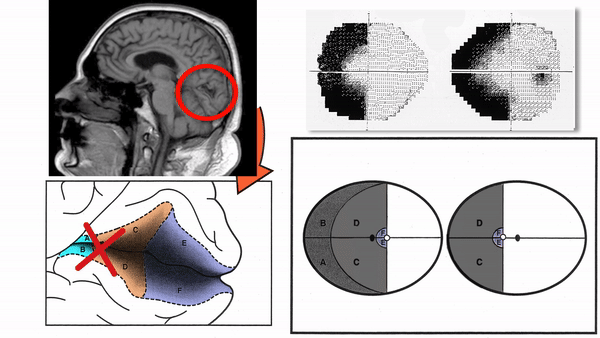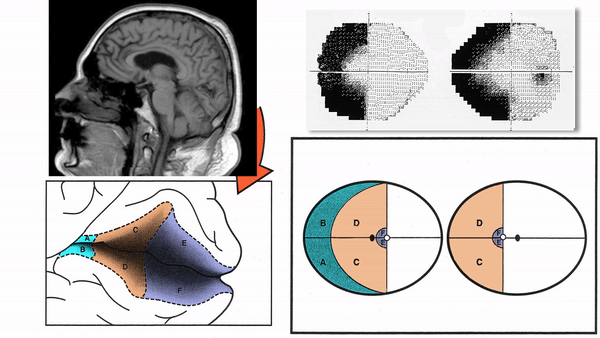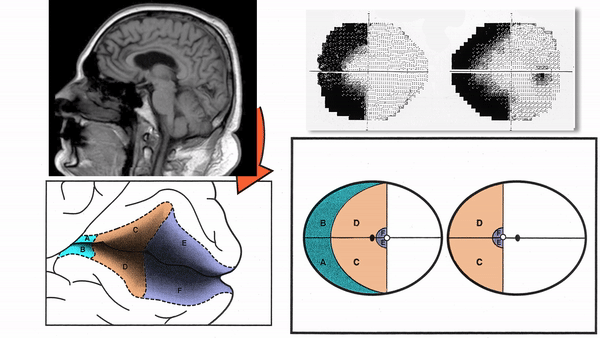
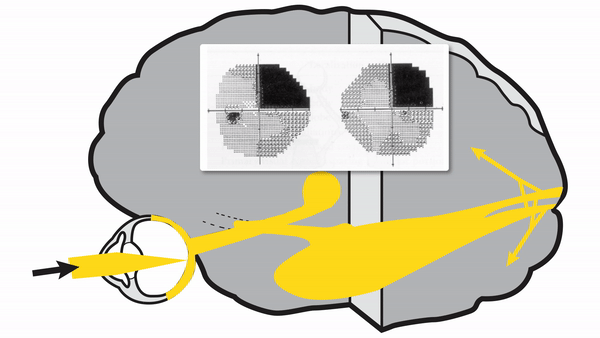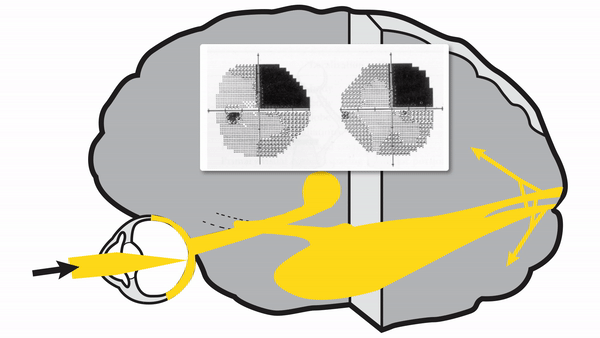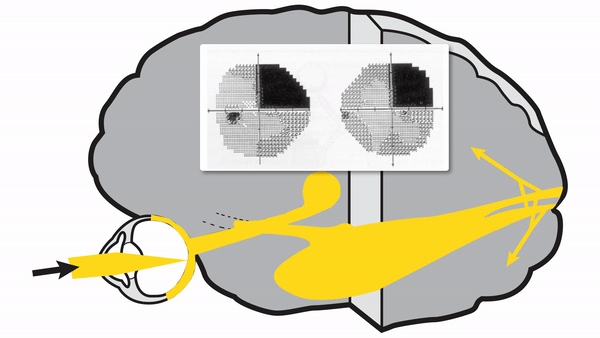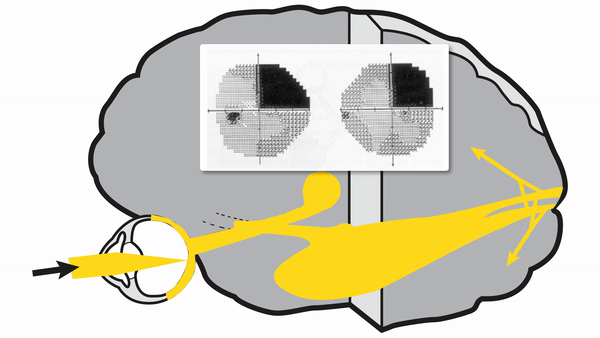
Meyer's loop lesions
- Produce superior wedge-shaped homonymous hemianopia, also called “pie-in-the-sky” defects
- Common cause is temporal lobectomy for intractable seizures
- Optic radiation lesions
-
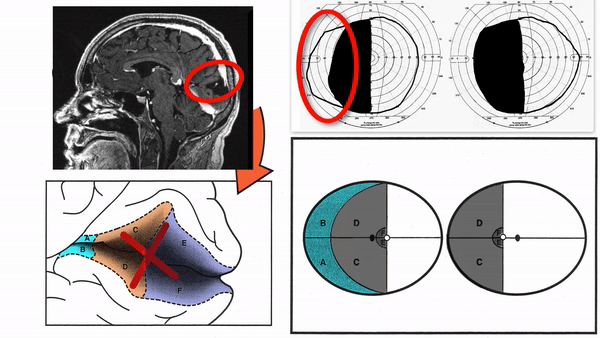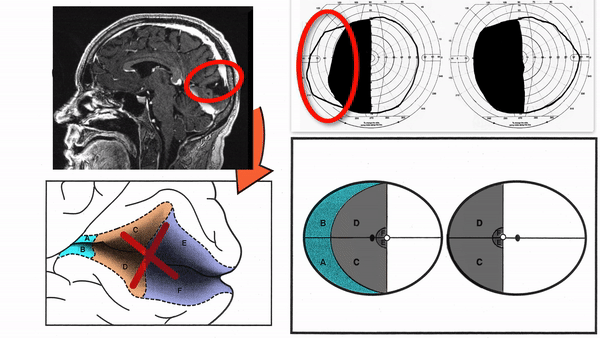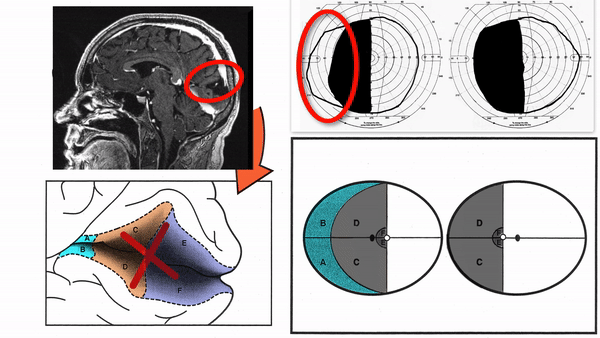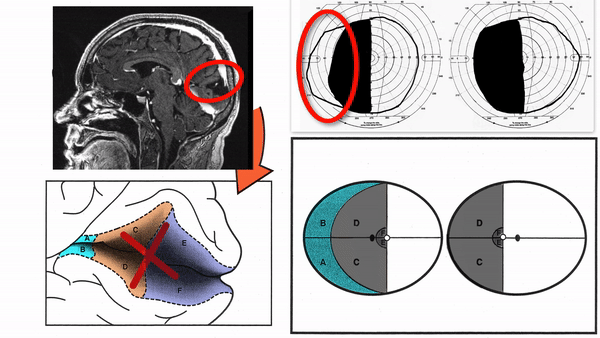
Primary visual cortex lesions
-
Produce complete homonymous hemianopias,
incomplete congruous homonymous hemianopias,
or the following other incomplete homonymous hemianopias
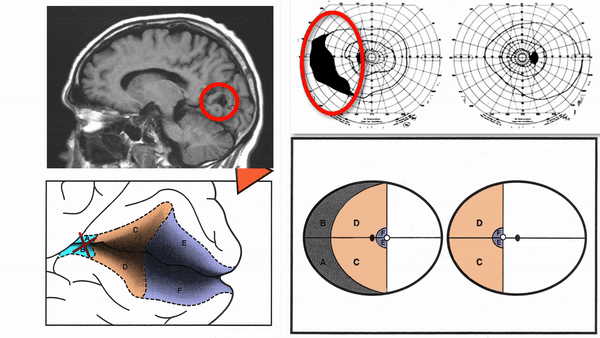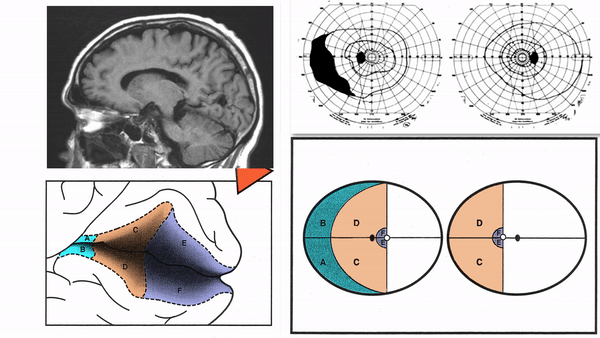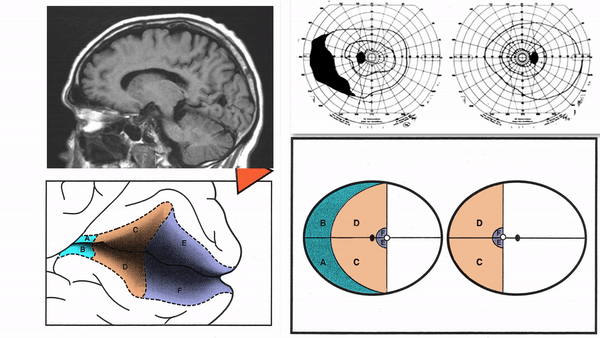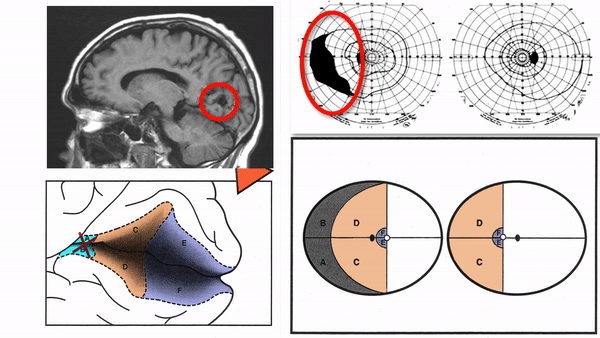
- Superior homonymous quadrantanopia (lesion damages only inferior visual cortex)
- Inferior homonymous quadrantanopia (lesion damages only superior visual cortex)
- Homonymous paracentral scotomas (lesion restricted to posterior visual cortex)
- Macular-sparing homonymous hemianopia (lesion restricted to midportion and anterior portion of visual cortex
- Temporal crescent-sparing homonymous hemianopia (lesion spares anterior visual cortex)
- Temporal crescent scotoma (lesion restricted to anterior visual cortex)


-
Produce complete homonymous hemianopias,
incomplete congruous homonymous hemianopias,
or the following other incomplete homonymous hemianopias