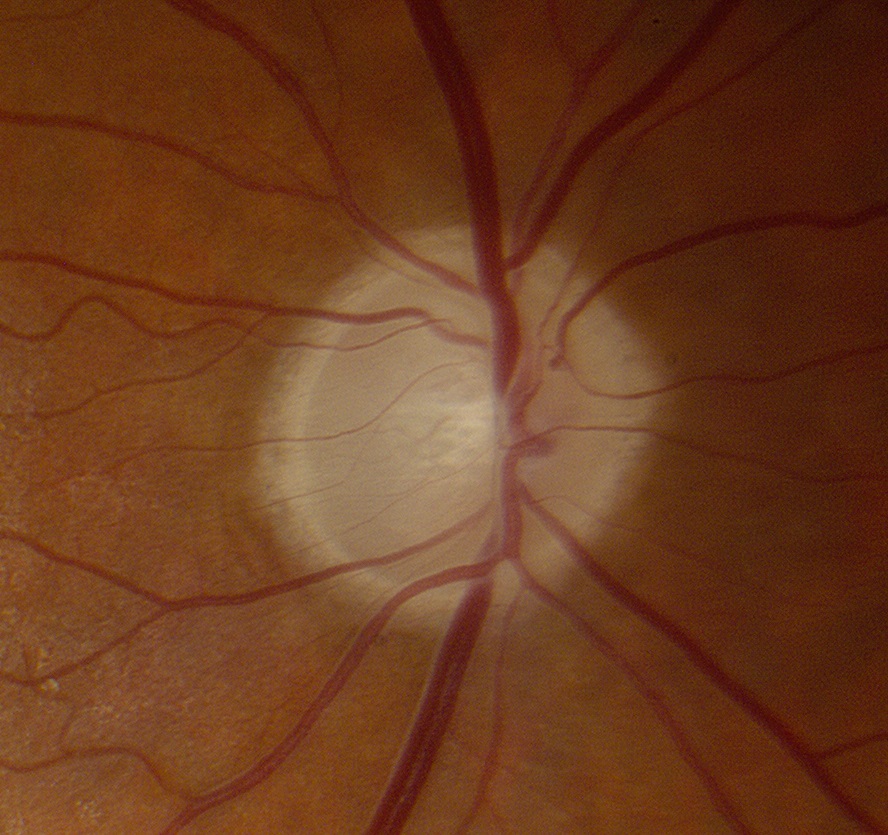
The Excavated Optic Disc
- Thinning (excavation) of the optic disc neuroretinal rim so that the optic disc appears pathologically cupped
- Common causes: primary open angle glaucoma, optic disc coloboma
- Uncommon causes: arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy, compressive optic neuropathy
- Focal or diffuse thinning of neuroretinal rim tissue
-
Glaucomatous excavation
- Rim thinning occurs first inferiorly, then superiorly, then temporally and finally nasally
- Residual neuroretinal rim retains its pink color
- Visual field nerve fiber bundle defects appear only when the neuroretinal rim becomes markedly thinned



-
Non-glaucomatous excavation
- Residual neuroretinal rim appears white
- Excavation is not as deep and the notching of the neuroretinal rim is not as great as in glaucoma

- Distinguish pathologic excavation of the optic disc from a large physiologic optic disc cup
-
Perform visual field examination
- Should be normal in large physiologic cupping
- Should show nerve fiber bundle defects in pathologic cupping, especially if advanced
- Document the optic disc appearance by photography and/or optical coherence tomography
- Schedule serial examinations to detect any increase in optic disc excavation or visual field loss
- Overlooking glaucoma may lead to avoidable blindness
-
Trap: misdiagnosis of a myopic tilt or optic disc coloboma as glaucoma leads to fruitless treatment with intraocular pressure-lowering agents
-
Trap: misdiagnosis of “non-glaucomatous cupping” as glaucoma leads to delayed diagnosis of potentially vision-threatening or life-threatening optic neuropathies



