( of )
Correct: 0
Incorrect: 0
A 17 year old man develops painless loss of vision in his left eye. He has been previously healthy, taking no medications, and without notable family history. Visual function is normal in the right eye, but markedly depressed in the left eye with an afferent pupil defect. This is the appearance of the left optic fundus. All other aspects of his clinical examination are normal.

Which of the following statements is true?
Correct!
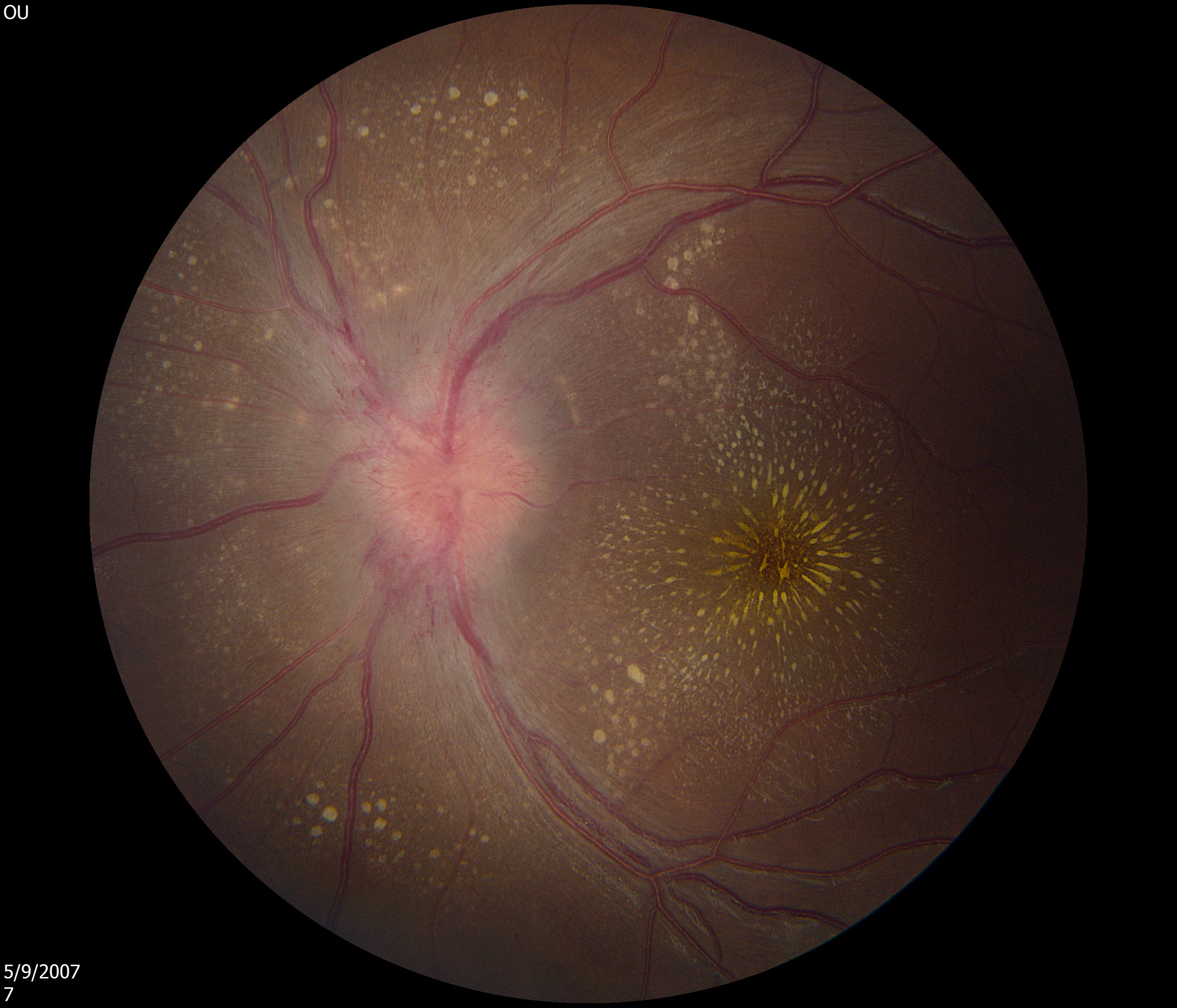 You are looking at a swollen left optic disc. At this patient’s young age, the mechanism is probably inflammation, and the condition is labeled
“papillitis.” It is a form of primarily intraocular (rather than retrobulbar) optic neuritis. Because trigeminal afferents do not penetrate that part of
the optic nerve, there is no periocular pain. Brain/orbit MRI may show enhancement of the optic disc and sometimes intraorbital parenchymal or dural
enhancement of the optic nerve. Perifoveal yellow exudates (“macular star”)
You are looking at a swollen left optic disc. At this patient’s young age, the mechanism is probably inflammation, and the condition is labeled
“papillitis.” It is a form of primarily intraocular (rather than retrobulbar) optic neuritis. Because trigeminal afferents do not penetrate that part of
the optic nerve, there is no periocular pain. Brain/orbit MRI may show enhancement of the optic disc and sometimes intraorbital parenchymal or dural
enhancement of the optic nerve. Perifoveal yellow exudates (“macular star”)
often become more apparent within 2 weeks after clinical onset, reflecting the intense leakage of papillary capillaries, and generating the label
“neuroretinitis,” although this condition is not really a retinal inflammation. An evaluation for systemic infectious (including syphilis and Lyme disease)
and non-infectious inflammatory disorders is reasonable. A positive Bartonella serum antibody often turns up, generating a presumption that cat scratch
disease is the cause. However, no other clinical evidence of that disease is typically found. If the Bartonella titer is elevated, patients may be treated
with doxycycline. If not, corticosteroid treatment is often employed, although there are no controlled trials to prove benefit of any treatment.
With regard to the other answer choices: multiple sclerosis does not develop when there is this much optic disc inflammation; substantial visual recovery occurs with or without treatment in 50% to 75% of cases; MRI does not usually show cerebral white matter abnormalities.

With regard to the other answer choices: multiple sclerosis does not develop when there is this much optic disc inflammation; substantial visual recovery occurs with or without treatment in 50% to 75% of cases; MRI does not usually show cerebral white matter abnormalities.
Incorrect
Incorrect