( of )
Correct: 0
Incorrect: 0
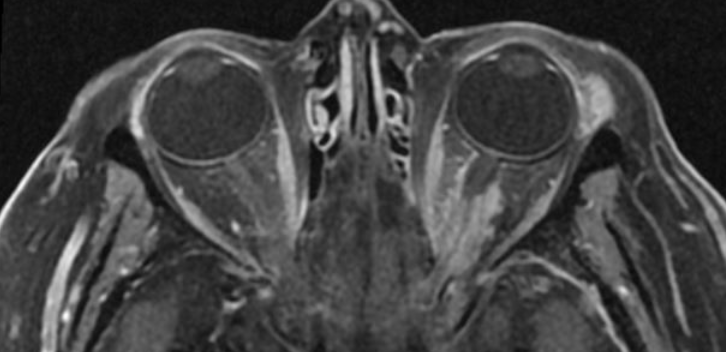
A 50 year old woman is found to have a best-corrected visual acuity of 20/50 (6/15, 0.40) in her left eye and 20/20 (6/6, 1.0) in her right eye on a routine optometric examination. Formal visual fields show a nerve fiber bundle defect in the affected left eye and a normal visual field in the right eye. There is an afferent pupil defect in the left eye, but otherwise the examination of both eyes is normal, including the appearance of both optic discs on ophthalmoscopy. Brain/orbit MRI shows this isolated abnormality.
What management do you recommend to the patient?
Correct!
The imaging features here suggest either an optic nerve sheath meningioma, a chronic dural inflammation (“pachymeningitis”), or lymphoma. The dilemma here
is that biopsy is certain to damage vision. Recommend it only if all vision has been lost for many months and diagnosis is in doubt.
Can else can you do to get closer to a diagnosis? You could order a CT scan, looking for calcium in the lesion, which would favor meningioma. You could order “pan CT scanning” to rule out inflammation or lymphoma elsewhere in the body. You could order a gallium 68 DOTATATE-PET scan, which binds to somatostatin receptors that are plentiful in neuroendocrine tumors and meningiomas. However, its specificity is not settled.
A trial of prednisone may be your best bet. If it improves vision, you would reasonably exclude meningioma. In that case, additional imaging would be indicated to try to distinguish between the other options. If not, you are probably dealing with meningioma.
X-irradiation probably reduces the chances of meningioma growth and further vision loss, and may even improve vision, but is not recommended if vision has already been severely compromised. If x-irradiation is to be carried out, make sure that it is done in a center with experience treating such lesions, otherwise radiation toxicity to the retina, optic nerves, and optic chiasm is a serious risk! Do not recommend x-irradiation to prevent growth of an intracranial component because lesions that originate in the orbit almost never show sufficient intracranial growth to damage the other optic nerve or optic chiasm.
Observation is an option here, except that vision loss is likely to occur eventually.
Can else can you do to get closer to a diagnosis? You could order a CT scan, looking for calcium in the lesion, which would favor meningioma. You could order “pan CT scanning” to rule out inflammation or lymphoma elsewhere in the body. You could order a gallium 68 DOTATATE-PET scan, which binds to somatostatin receptors that are plentiful in neuroendocrine tumors and meningiomas. However, its specificity is not settled.
A trial of prednisone may be your best bet. If it improves vision, you would reasonably exclude meningioma. In that case, additional imaging would be indicated to try to distinguish between the other options. If not, you are probably dealing with meningioma.
X-irradiation probably reduces the chances of meningioma growth and further vision loss, and may even improve vision, but is not recommended if vision has already been severely compromised. If x-irradiation is to be carried out, make sure that it is done in a center with experience treating such lesions, otherwise radiation toxicity to the retina, optic nerves, and optic chiasm is a serious risk! Do not recommend x-irradiation to prevent growth of an intracranial component because lesions that originate in the orbit almost never show sufficient intracranial growth to damage the other optic nerve or optic chiasm.
Observation is an option here, except that vision loss is likely to occur eventually.
Incorrect
Incorrect