( of )
Correct: 0
Incorrect: 0

A patient with a left Horner syndrome, together with hypertropia and ipsilateral ataxia, is most likely to have a lesion in
Incorrect
Incorrect
Incorrect
Correct!
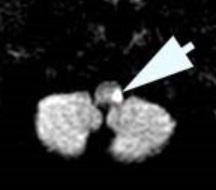 The combination of Horner syndrome, hypertropia (from skew deviation), and ataxia is strong evidence of a lesion in the dorsolateral medulla. In that
region, infarction is the overwhelmingly likely cause, secondary to occlusion of the ipsilateral vertebral artery and its posterior inferior cerebellar
artery branch.
The combination of Horner syndrome, hypertropia (from skew deviation), and ataxia is strong evidence of a lesion in the dorsolateral medulla. In that
region, infarction is the overwhelmingly likely cause, secondary to occlusion of the ipsilateral vertebral artery and its posterior inferior cerebellar
artery branch.
A stroke in this territory, known as the “Wallenberg syndrome,” is often caused by idiopathic or traumatic dissection of the vertebral artery. The infarction may include the inferior cerebellum. If the cerebellum swells, it may compress the medulla, creating an aspiration risk and a neurologic emergency. The damaged cerebellum may have to be surgically excised.
This is the most common brainstem stroke at any age, but especially in young adults.

A stroke in this territory, known as the “Wallenberg syndrome,” is often caused by idiopathic or traumatic dissection of the vertebral artery. The infarction may include the inferior cerebellum. If the cerebellum swells, it may compress the medulla, creating an aspiration risk and a neurologic emergency. The damaged cerebellum may have to be surgically excised.
This is the most common brainstem stroke at any age, but especially in young adults.